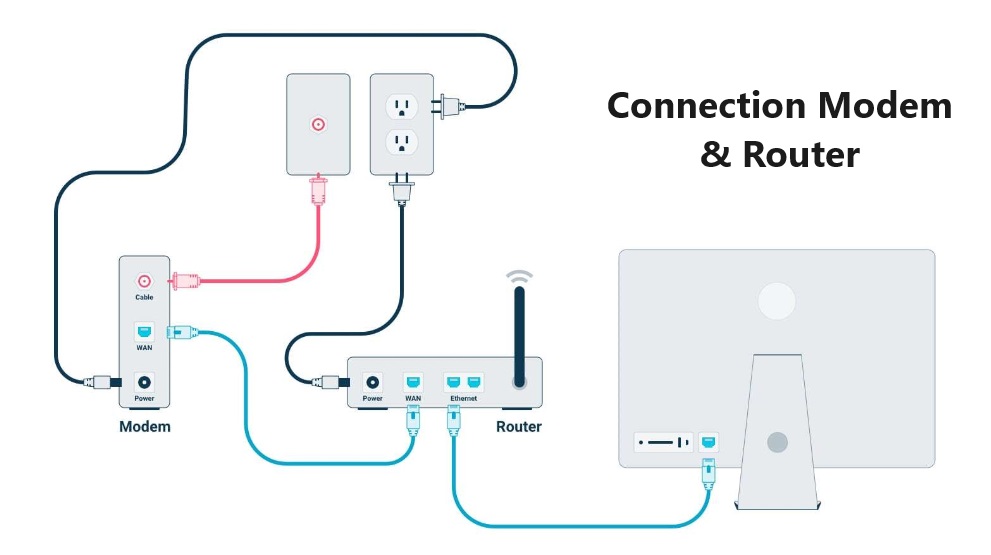
It is easy to connect router and modem with your internet service providers. Either you can accomplish it by matching cable plug color or follow below steps to establish Modem to router cable connection. You will be your own tech consultant.
Modem to router cable connection YouTube tips
Required cables for Modem to router cable connection
You will need the following in order to use an Ethernet cable to connect a modem and router to your computer.
- Router
- Modem
- Two Ethernet wires
- Coaxial wire
- Power cords for modems and routers
You must unplug your old modem from your computer and cable wall outlet before installing your new one.
Easy steps to connect modem to router
Attach the coaxial cable’s opposite end to the modem after plugging the first end into the cable wall socket.
After plugging one end of the modem power cord into an outlet, attach the other end to the modem.
Attach one end of an Ethernet cable to the modem’s back, and the other end to the router’s Wide Area Network (WAN) port.
After plugging one end of the router power cord into an outlet, attach the other end to the router.
Attach the other end of the second Ethernet cable to the rear of the computer and plug it into port 1 on the router.
Verify the power supply to the modem and router by looking at their lights, then connect your computer to the network.
- Consult the user manuals or support webpages from the manufacturer to find out more about which light is on for your particular gadgets.
There are a few security measures you should implement to safeguard your wireless network after connecting your router to a modem. Changing the router’s default Wi-Fi password is the first step towards safeguarding your privacy. By doing this, hackers may be unable to access your network. Changing the password requires logging into your router.
By opening a web browser or app, typing your router’s IP address into the search bar, and then checking in with your username and password, you may modify the router’s settings. To protect privacy, you can create guest networks and change passwords there.
Which cable is better ?
Adding new wireless devices to your home Wi-Fi network is simple and doesn’t require additional wires once it is set up. However, there are some circumstances in which having physical links could be preferable.If it makes sense to you, here’s how to find out.
A wired connection is dependable
Generally speaking, a cable connection is more dependable than Wi-Fi. Your router’s Wi-Fi signal is vulnerable to obstructions and interference, which can result in poor signal quality, sluggish speeds, and other problems. The shielding of the cable provides protection for your signal against these possible hindrances when you use a wired Ethernet connection. In addition to offering greater consistency in speed and a more seamless online experience, wired connections also tend to be more dependable and have fewer drops.
Greater speed
Your computer’s connection speed may be increased by connecting it directly to your router via an Ethernet cable as opposed to using Wi-Fi.
Optimizing gigabit connectivity
If you’ve been using DSL or satellite internet, upgrading to gigabit internet will result in a significant speed increase. However, if your router isn’t able to broadcast a gigabit Wi-Fi signal, it won’t be very helpful. We strongly advise upgrading to a gigabit router if you currently pay for gigabit internet.
However, make sure that your computer is plugged into your present router in the interim if you’re taking your time weighing your alternatives or are simply saving up for the router you truly want. Ethernet cables (CAT5e and up) can handle your connection speed even if your Wi-Fi cannot. If you can locate an ISP that supports multigigabit rates, CAT6a, CAT7, and CAT8 connections have the potential to handle even higher speeds.
Naturally, the type of cable you use won’t matter if the Ethernet ports on your router can only handle 100 Mbps.
Keep away the dead zones
Although connecting via Wi-Fi is far more easy than using physical wires, there is a drawback: dead zones are common in Wi-Fi networks. There are two main options available to you for handling these problematic locations.
Option 1: Purchase Wi-Fi extenders.
Wi-Fi signals from your router are replicated by the majority of Wi-Fi extenders. This might result in a sharp drop in speed, usually in half. However, in some circumstances, Wi-Fi extenders might be an inexpensive, efficient, and simple solution.
Option 2: Run Ethernet wiring throughout your house.
You can hire a contractor or professional to run Ethernet wire throughout your house, or you can do it yourself.
Since they don’t involve soldering, Ethernet cables are rather straightforward to create and reasonably inexpensive. A single Wi-Fi extension can cost less than $1,000 for 1,000 feet of sophisticated CAT6 cable if you’re tech-savvy enough to attach your own connectors and want to physically wire your entire house with Ethernet.
Cutting down on latency
When constructing a home network, signal strength and speed are the most important factors to consider, yet connected connections always outperform Wi-Fi in one area: latency.
Editor’s recommendations
- Which TP Link Deco mesh is best – comparison?
- Compare TP-Link Deco X55 Vs X60 Specs & Price
- TP-Link Deco AX3000 WiFi 6 Mesh System(Deco X55) Review
- Google Nest WiFi 4-Pack Review – What Is The Best Price?
- Compare Motorola MB8611 Vs Arris S33 – Which Has More Speed?
- Motorola MB8611 Docsis 3.1 Review – Should You Buy It?